By Sivaji | SAP Commerce by Sivaji
SAP Commerce Cloud is a powerful e-commerce platform used by enterprises worldwide. Whether you’re a developer, consultant, or enthusiast, getting started can feel overwhelming due to its rich features and complex architecture. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to start your journey with SAP Commerce Cloud.
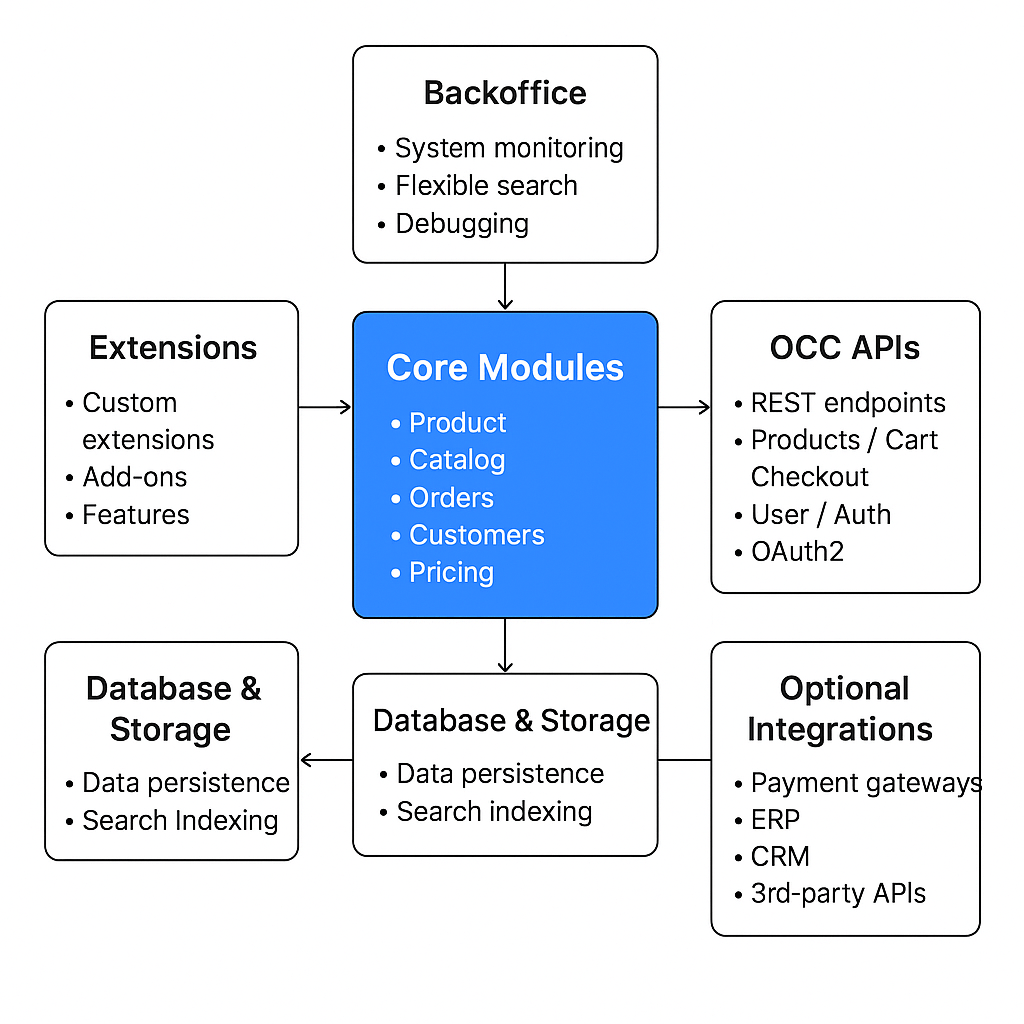
1. Understand the SAP Commerce Cloud Architecture
Before diving into development, it’s important to understand its architecture:
- Core Modules: Handles main e-commerce logic like products, orders, and carts.
- Extensions: Modular features that can be customized or extended.
- Backoffice & HAC: Admin interfaces for managing data and performing tasks.
- OCC APIs: RESTful APIs for headless integration with frontend or mobile apps.
💡 Tip: Familiarize yourself with the official SAP Commerce documentation—it’s your best friend.
2.Setting Up Your Development Environment
Step-by-step setup:
- Install Java Development Kit (JDK) – SAP Commerce typically requires JDK 17+ depending on your version.
- Install Apache Ant – Required for building the platform.
- Install an IDE – IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse is recommended.
- Download SAP Commerce Cloud – Obtain the installer from the SAP Support Portal.
Once installed, you can start the server and access the Backoffice at:
https://localhost:9002/backoffice
3. Creating Your First Extension
Extensions are modular pieces of functionality. Follow these steps to create one:
# Navigate to your SAP Commerce installation directory
cd <HYBRIS_HOME>/bin/platform
# Generate a new extension using ant
ant extgen
- Choose “y” for standard template
- Name your extension (e.g.,
mysitecore) - Follow the prompts, then build your project:
ant clean all
4. Accessing the Backoffice and HAC
- Backoffice: Admin interface for managing products, categories, and users.
- HAC (Hybris Administration Console): For performing system tasks, debugging, and running flexible search queries.
💡 Tip: Use flexible search in HAC to query your database efficiently without writing raw SQL.
Example query:
SELECT {code}, {name} FROM {Product}
5. Explore OCC APIs
SAP Commerce offers REST APIs via the OCC (Omnichannel Commerce Connect) framework. These APIs enable headless integrations.
Example: Fetch products using the REST API:
GET https://localhost:9002/rest/v2/{baseSiteId}/products
Use Postman or curl to test API endpoints before integrating them with your frontend.
6. Best Practices for Beginners
- Always work in a local development environment before deploying to staging/production.
- Keep your extensions modular to avoid tightly coupled code.
- Use version control (Git) for tracking changes.
- Learn to use flexible search queries instead of raw SQL.
- Keep customizations minimal to simplify future upgrades.
Conclusion
Starting with SAP Commerce Cloud may seem complex at first, but by understanding the architecture, setting up a proper environment, and learning the basics of extensions and APIs, you’ll be ready to build robust e-commerce solutions.
This is just the beginning of your SAP Commerce journey. Stay curious, explore different modules, and gradually dive into advanced topics like integration with third-party services, performance tuning, and headless implementations.
In upcoming posts, I’ll dive deeper into:
- Deep drive on SAP Commerce Code Architecture.
- How to create custom extensions
- Building OCC APIs
- Performance tuning tips

Leave a comment